ACT - Advanced Cooling Technologies
Advanced Cooling Technologies & Lincoln Associates
Founded in 2003, Advanced Cooling Technologies (ACT) has established itself as a leader in the design and manufacturing of advanced thermal management solutions. With a focus on HVAC energy efficiency, ACT offers innovative solutions that help businesses reduce energy costs, improve energy recovery, and minimize environmental impact.
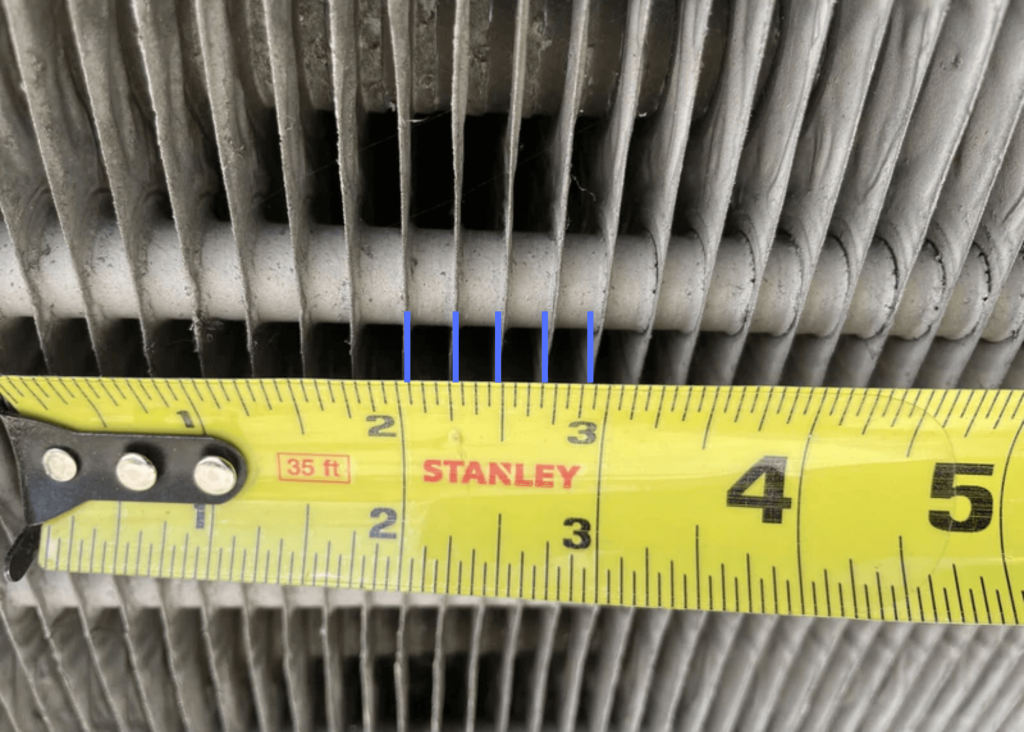
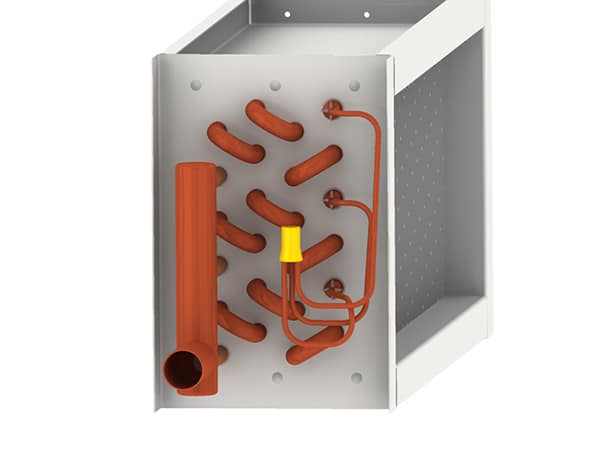
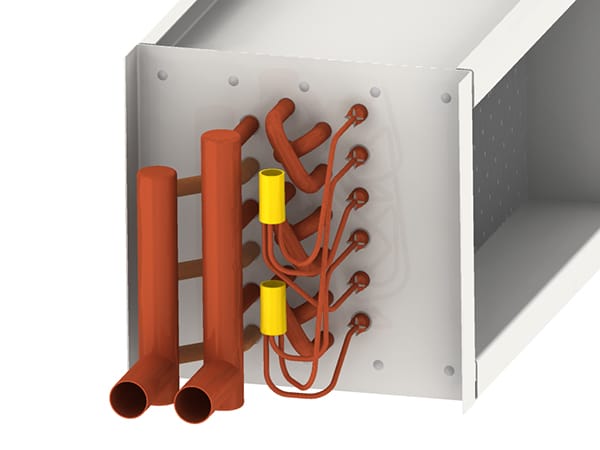
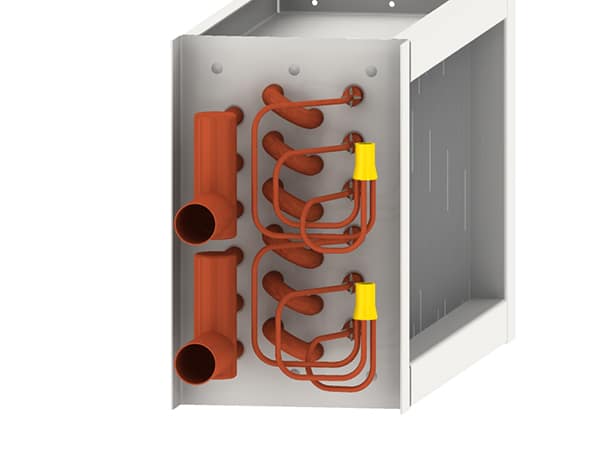
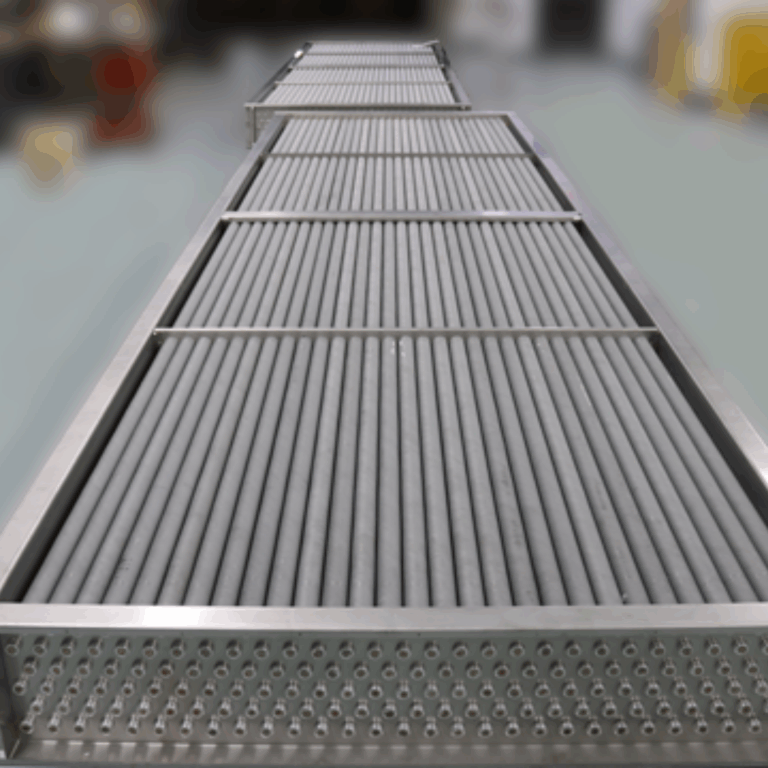
For over two decades, ACT has been dedicated to providing cutting-edge passive heat pipe technology to the HVAC industry. Their signature Heat Pipe Heat Exchangers offer a smarter, more efficient alternative to traditional mechanical energy wheels, delivering up to 70% energy savings and a typical payback period of just two years. Designed with no moving parts, these systems maximize HVAC energy recovery, improving overall efficiency while eliminating the need for motors, belts, and bearings. This results in significant maintenance reduction and improved long-term performance.

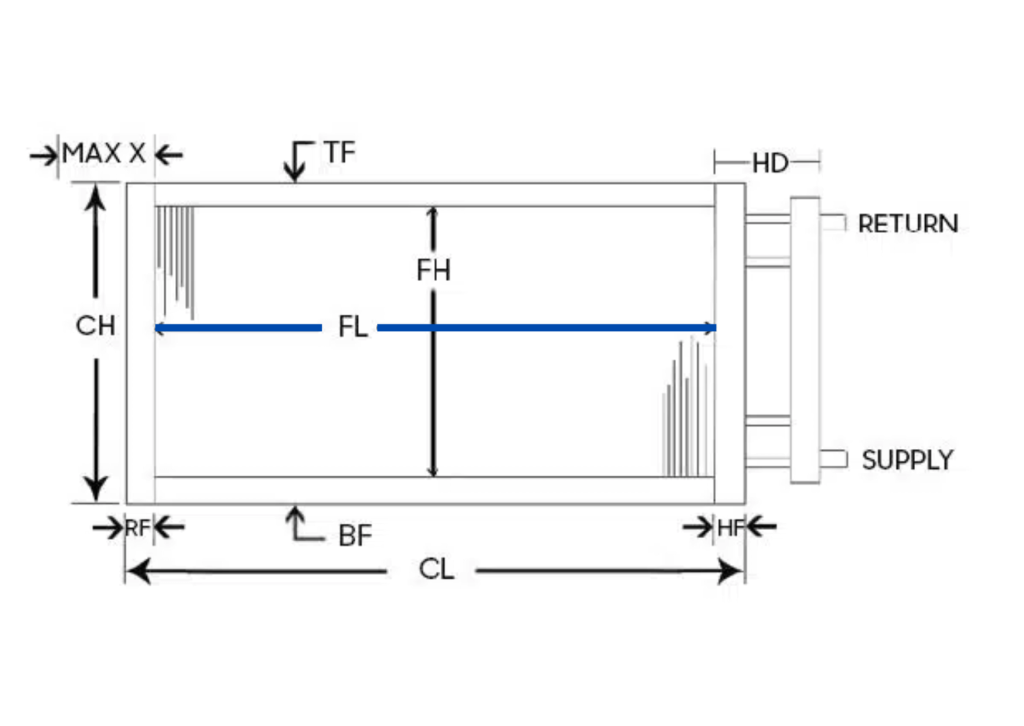
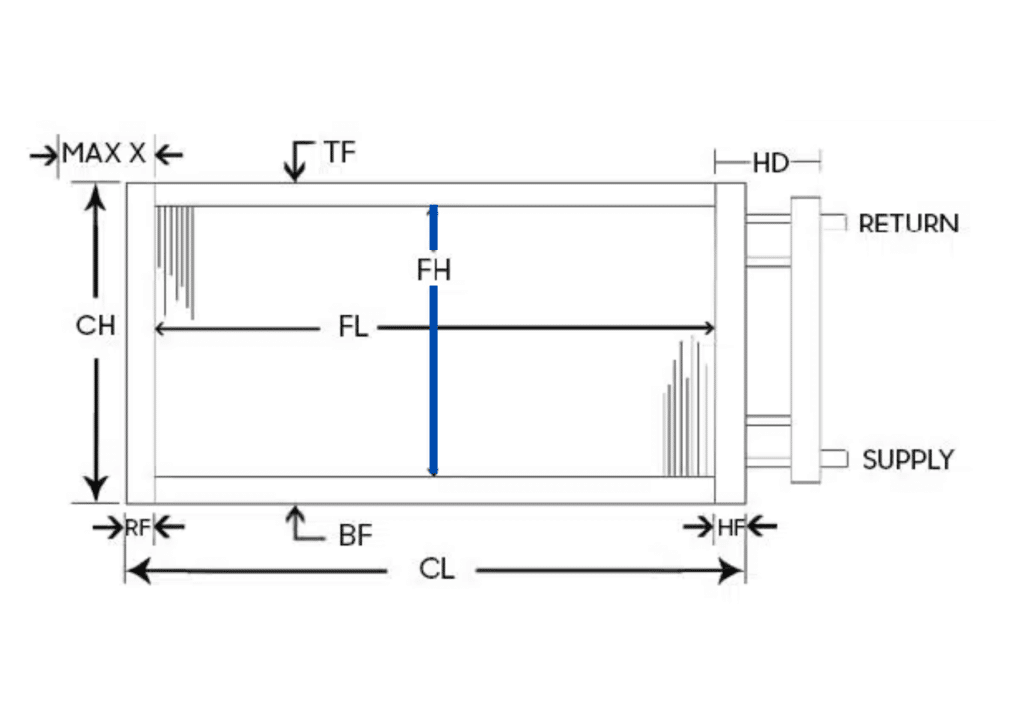
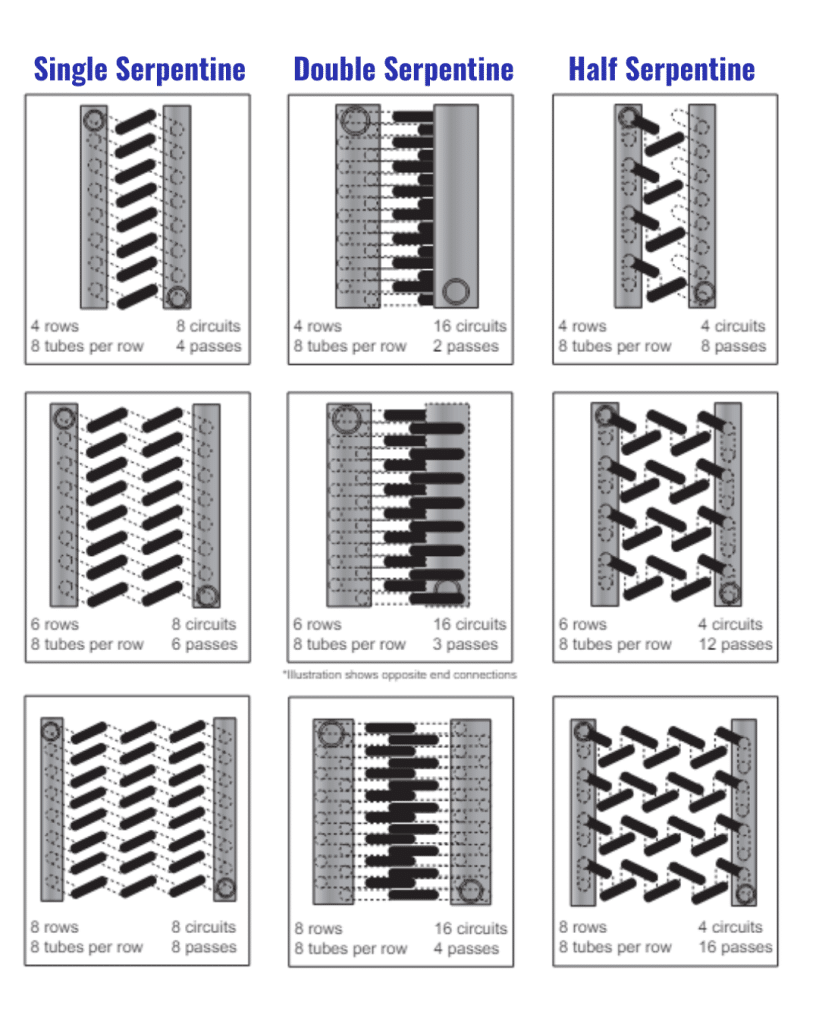
How Heat Pipe Heat Exchangers Work
ACT’s Heat Pipe Heat Exchangers (HPHX) use advanced passive heat pipe technology to recover waste heat and improve energy efficiency in HVAC systems. Unlike traditional mechanical systems, which rely on moving parts, Heat Pipe technology operates with no motors, belts, or bearings.
By transferring heat through a sealed, liquid-filled pipe, the system efficiently captures and redistributes thermal energy, reducing the need for additional cooling or heating inputs. This design ensures high efficiency, low maintenance, and long-term reliability, making it a perfect fit for HVAC applications in various industries.
Key Benefits for HVAC Systems
Energy Recovery
Efficiently recovers and reuses waste heat, optimizing HVAC system performance and reducing operational energy costs.
Reduced Maintenance
Eliminates moving parts like motors and belts, leading to lower maintenance costs and extended system life.
Sustainability
Helps reduce carbon emissions and promotes energy-efficient building operations, contributing to environmental sustainability.
Cost Savings
Achieves up to 70% energy savings, delivering a typical payback period of just two years, resulting in significant long-term savings.
Industries Served
ACT’s HVAC solutions are ideal for a wide range of industries, including:
Commercial Buildings: Improving HVAC performance in office buildings, retail spaces, and hotels, while reducing energy consumption and costs.
Industrial Facilities: Enhancing HVAC energy recovery in manufacturing plants, warehouses, and distribution centers to support operational efficiency.
Healthcare: Ensuring precise temperature and air quality control in hospitals, medical offices, and research labs, with minimal energy waste.
Data Centers: Providing efficient cooling solutions for IT infrastructure, optimizing HVAC systems and reducing operating costs.


Lincoln Associates
-
800 Battery Ave SE, Ste 300
Atlanta, GA 30339 -
(770) 425-1500(770) 425-1500
- [email protected]
Contact Lincoln Associates Today.
*Our Customer Support Team will contact you within 24 hours during normal business operations.